Samplation has often been a pain for Universal Analytics users. With the move to Google Analytics 4, the quotas for queries have been greatly increased. In GA4, the quota limit for event-level queries is 10 million events for standard Google Analytics properties and up to 1 billion events for Google Analytics 360 properties. This enables GA4 users to report on large timeframes and multiple dimensions without any sampling.
However, GA4 users often experience issues while reporting on small timeframes. This is because GA4 applies data thresholding in many cases to prevent anyone viewing a report or exploration from inferring the identity or sensitive information of individual users based on demographics, interests, or other signals present in the data.
What is the difference between data sampling and data thresholding?
Sampling:
- Definition: Sampling involves taking a subset or a portion of the data for analysis instead of processing the entire dataset.
- Purpose: Sampling is often used when dealing with large datasets to reduce processing time and resource usage.
- Impact: While sampling can speed up analysis, it may introduce some level of approximation or uncertainty, especially when dealing with outliers or specific patterns that might not be represented in the sampled subset.
Thresholding:
- Definition: Thresholding generally refers to the application of a threshold or a limit, often in the context of data processing or decision-making.
- Purpose: In analytics, thresholding may be applied to filter or limit the data based on certain criteria. For example, a threshold might be set to exclude data points below a certain value from being included in a report.
- Impact: Thresholding can influence the granularity and detail of the data being analyzed. It's a way to focus on specific aspects or segments of the data.
For GA4 users, this means that if you analyze a small timeframe and break it down by some dimension, some lines and cells in your report might not be filled with any data or removed from the report.
What can GA4 users do to avoid thresholding of the data?
In order to avoid data thresholding, it is possible to switch the reporting identity to device-based instead of using the blended reporting identity that is enabled by default. The downside of this switch is that GA4 will count users using only the cookies set on browsers and will not take into account the UserID if you have implemented it. This means the user will not be identified as the same user on multiple devices.
To do this, you need to navigate to Admin > Data display > Reporting Identity > Show all and switch to Device-based.
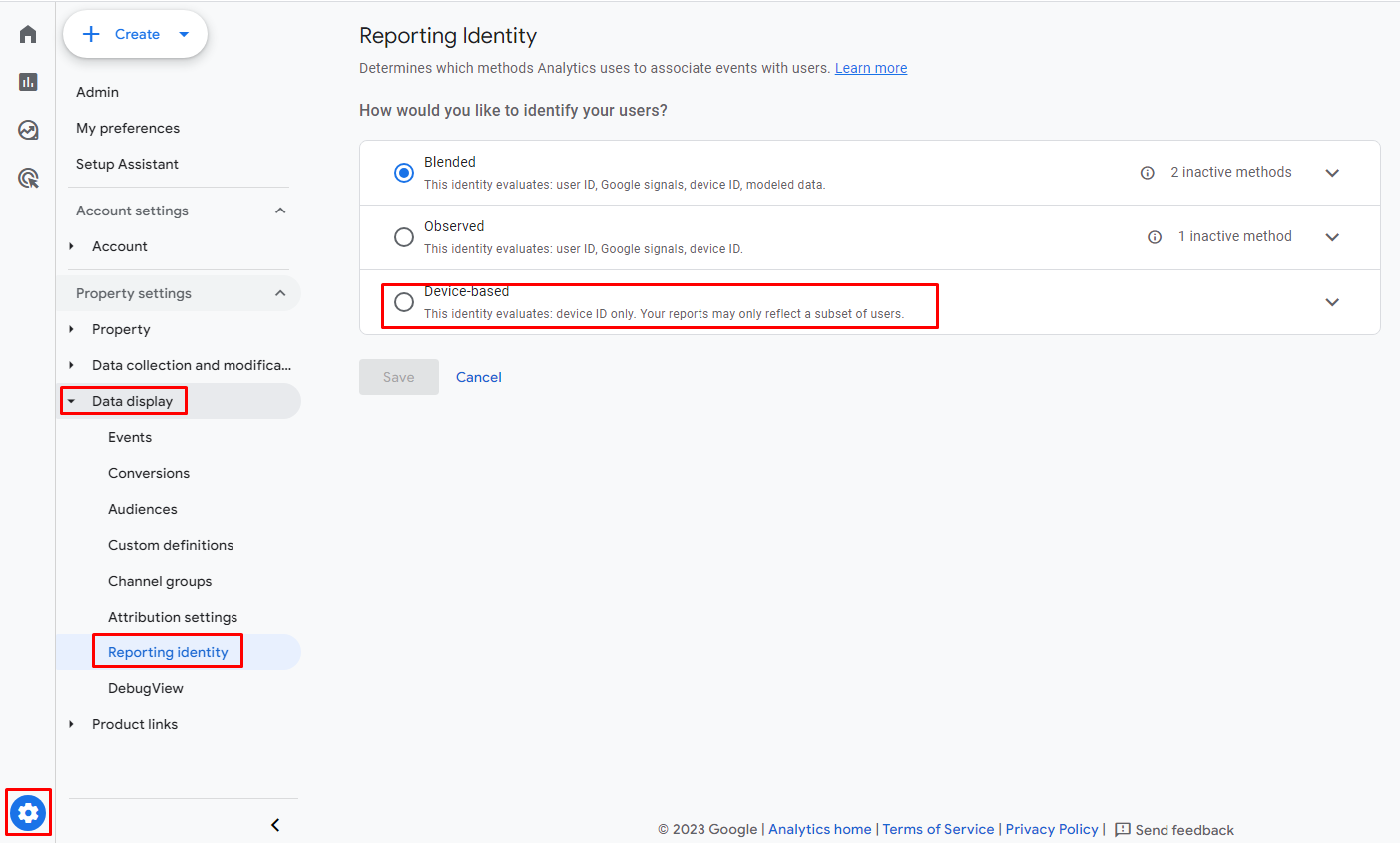
You can switch reporting models as needed, even after creating an exploration. Google Analytics will change the reporting identity in real-time, and you can switch the reporting models as many times as you need. When you have created an exploration, you can further view it with different reporting models.
The dark side of this is that reporting identity will be switched for all GA4 users. So, someone working with GA4 from a different account might find some strange changes in data if you switch the reporting identity while they are building some reports or explorations.
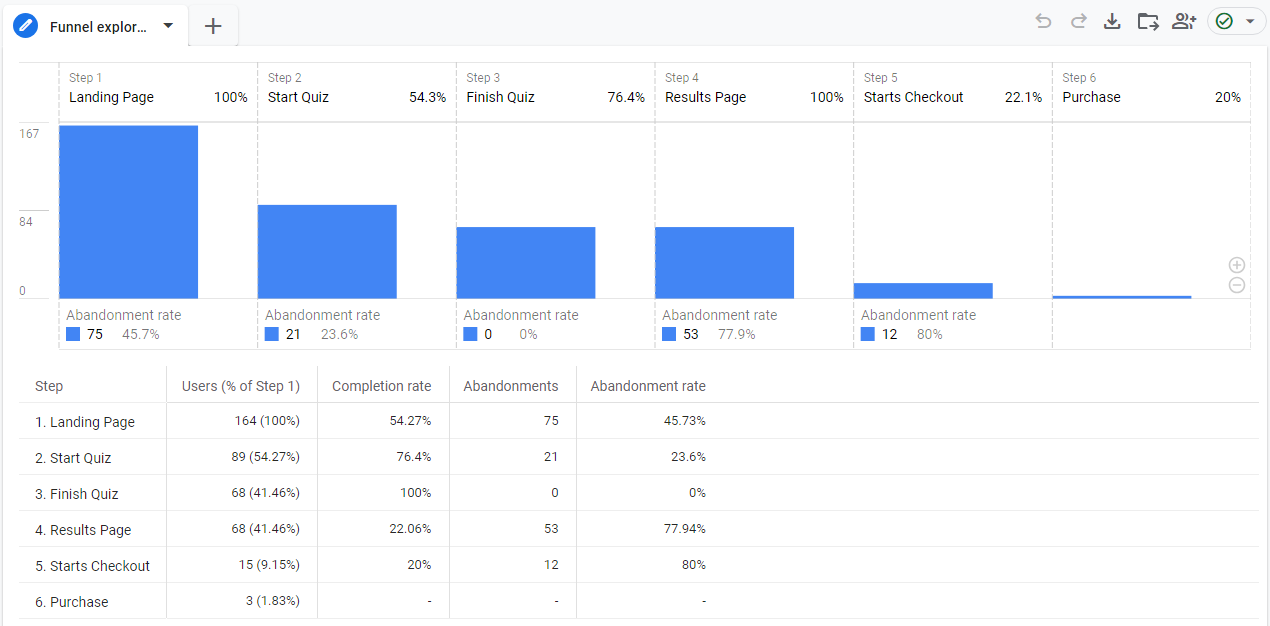
Here is an example of a funnel report with Threshold applied (blended reporting identity).
And the same report for the same GA4 data and timeframe but built for device-based reporting identity and without the threshold applied.
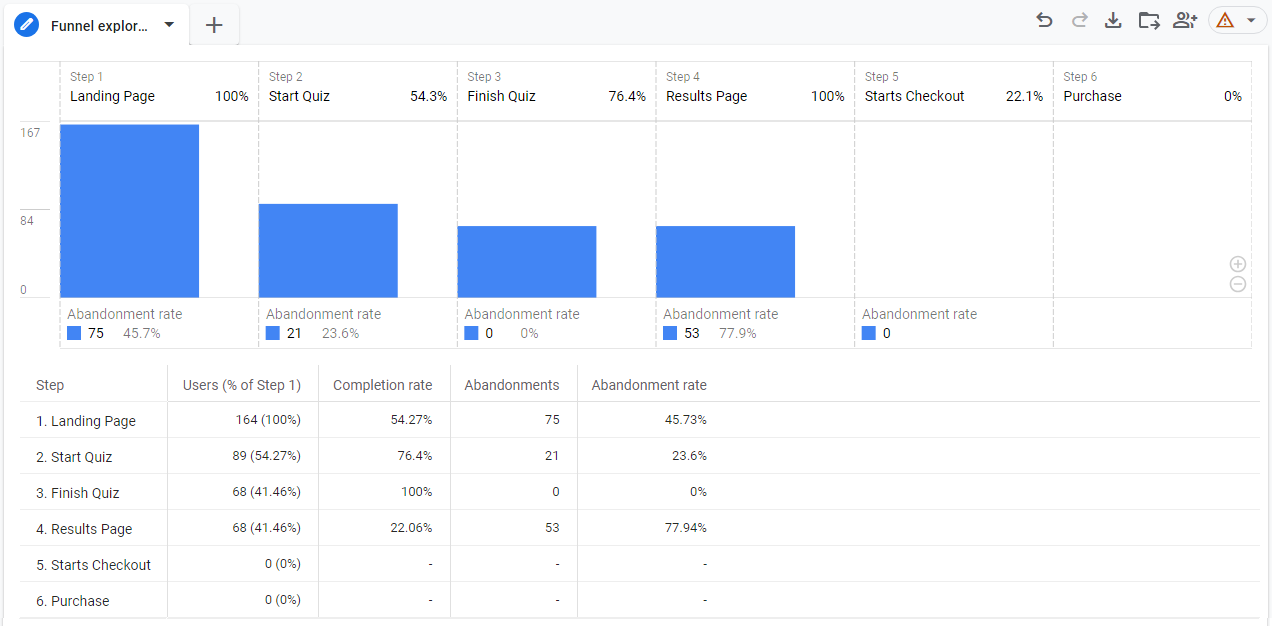
As you can see, when a threshold is applied, the last two lines (steps 5 and 6) do not have any data. This might lead to confusion that there were no purchases in this funnel.
Google Signals
Switching to device-based reporting is a hotfix, but for businesses actively promoting on mobile devices or with mobile apps, it might not be suitable. Another option is to exclude Google Signals from the reporting identity.
Google Signals is a feature within Google Analytics that enables additional cross-device tracking and reporting. Google Signals leverage signed-in users and their associated Google accounts to provide insights into user behavior across different devices.
To exclude Google Signals from the Reporting Identity, navigate to Admin > Data collection and modification > Data collection page and disable the "Include Google signals in reporting identity" switch.
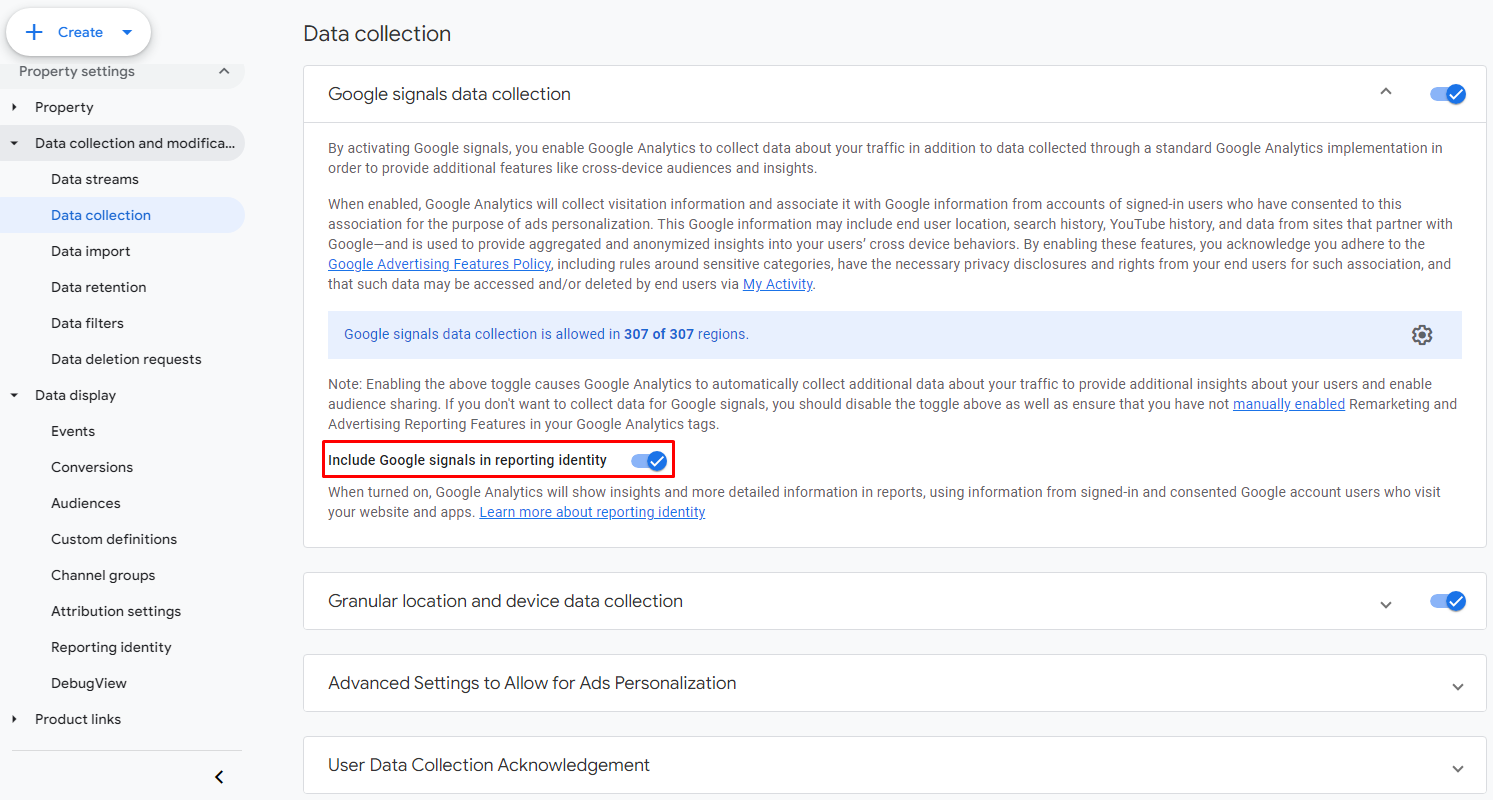
This is a recommended action. If you don't take this step manually, Google will handle it for you, albeit a bit later. According to an official announcement from Google, Google Signals will be removed from the reporting identity on February 12, 2024. This change will impact all Google Analytics 4 properties, affecting reporting features exclusively.
For reports without sampling or thresholding limitations, and the ability to leverage multiple attribution models, consider linking your GA4 data to BigQuery. BigQuery, Google's enterprise data warehouse, offers an unfiltered view of your GA4 data, free from sampling or thresholds.
Integrating BigQuery data with Looker Studio makes it easy to generate user-friendly reports. These reports can utilize more complex data structures. By using SQL queries, you can directly access data in BigQuery and display it in Looker Studio, create customized views, blend GA4 data with other sources, and process it in a way that suits your needs.
Another notable opportunity is harnessing AI for insights from your BigQuery data. But this is a large topic that deserves a separate blog post.

Leave a comment